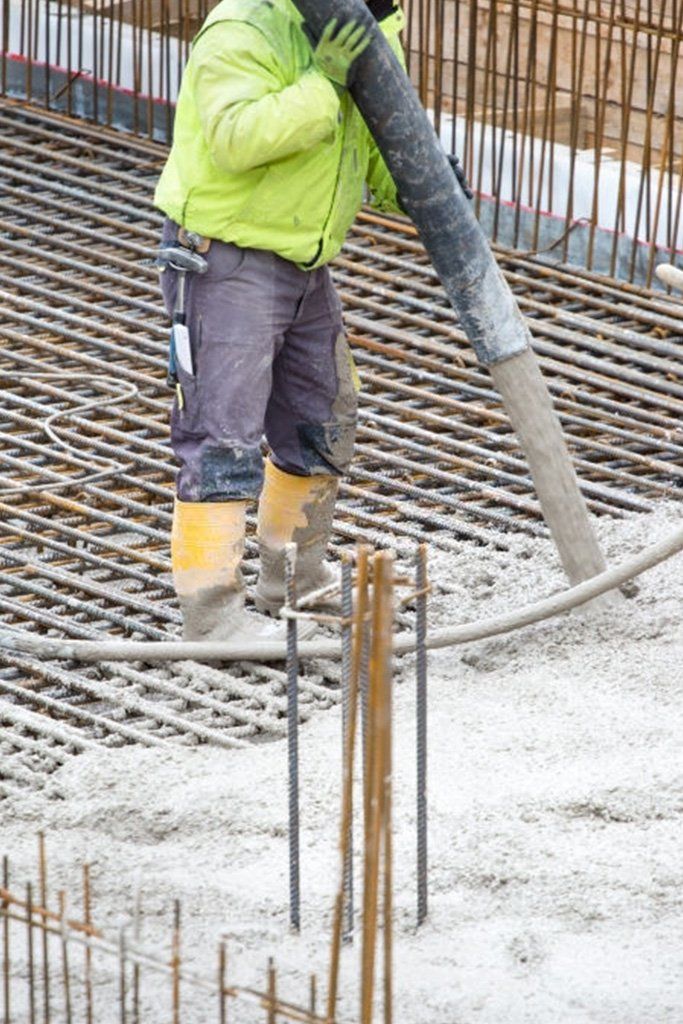
Concrete Foundation Hampton, VA
Building construction can benefit from concrete's strength and flexibility, ease of moldability, and cost-effectiveness. Making a concrete slab involves making a wooden frame in similar proportions to the shape of the concrete. Once the foundation has been excavated, the frame is placed inside the hole. Once the concrete is still wet in the frame, pour the mixture into the hole. Concrete will be poured into the hole. If you want to make the slab more robust, you can reinforce it with steel to ensure that it can handle more force and weight.
However, concrete has some weaknesses even though it is extremely strong. As a result of prolonged wet weather,
concrete may crack when damp conditions persist. One must check concrete periodically in order to detect possible damage and fix it as soon as possible. Cracks should also be filled in prior to becoming too large and threatening the structural integrity of a building.
Various types of concrete foundations exist. Why is it important to understand the differences? You could save both short-term and long-term time and money by applying this technique. Using one or the other has its advantages and disadvantages depending on how and where it is used.
3 Types of Foundations
1. T- Shaped Concrete Foundation
Typically used when there is a need to support structures in areas with frozen ground, there are several types of foundations. Normally, the frozen ground exerts pressure on foundations, but the T-shape foundation's unique design makes it resistant to this pressure.
Most construction projects start with a section of flat-footing placed below the anticipated frost line, then add walls on top of that. It is important to have walls that are not as wide as the footings so as to provide an additional level of support for the building's foundation. Ensure the walls of the building are not as wide as the footings so that the foundation is supported in an additional way. As well as being resistant to freezing ground effects, the T-shaped foundation is also renowned for its stability.
2. Slab-on-grade Foundation
Although this type of concrete foundation is also widely used, it is often used in areas where there is no freezing ground, so a T-shaped foundation is not required. In slab-on-grade construction, concrete is poured in one layer several inches thick.
You should pour the slab thicker at the edges so that it will provide a more stable foundation. Reinforcing rods are then used to give the thickened edge extra strength. The slab should be resting on a crushed gravel bed in order to improve drainage. Concrete can also be reinforced with a wire mesh to prevent cracks from occurring. It can still be reinforced with insulation to prevent frost damage even though slab-on-grade is ideally designed for places where the ground does not freeze.
3. Frost Protected Shallow Foundation
By counteracting frost-related effects, it is intended to counteract potential damage. The foundation uses natural heat energy from the earth and heat loss from the building to maintain its temperature. It usually ranges from 12 to 16 inches below grade for a Frost Protected Shallow Foundation (FPSF). In addition to preventing damage from freezing, it can also greatly reduce your excavation costs.
Those are the types of foundations that you can choose from. Think wisely and study every foundation so you can know what best fits your home. We have some expert specialists in our company that can help you with your project. We have installers, builders, pourers, leveling, and flooring that can do all the jobs at once for faster progress. We have one of the best subcontractors who provide affordable services. We will do everything polished and decorative for you; the work will be of high quality.
Are you looking for a “concrete foundation near me”? Contact us today!
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.

Copyright Concrete Guys Hampton | Proudly Powered by Snapps