How Thick Is The Parking Lot Cement?
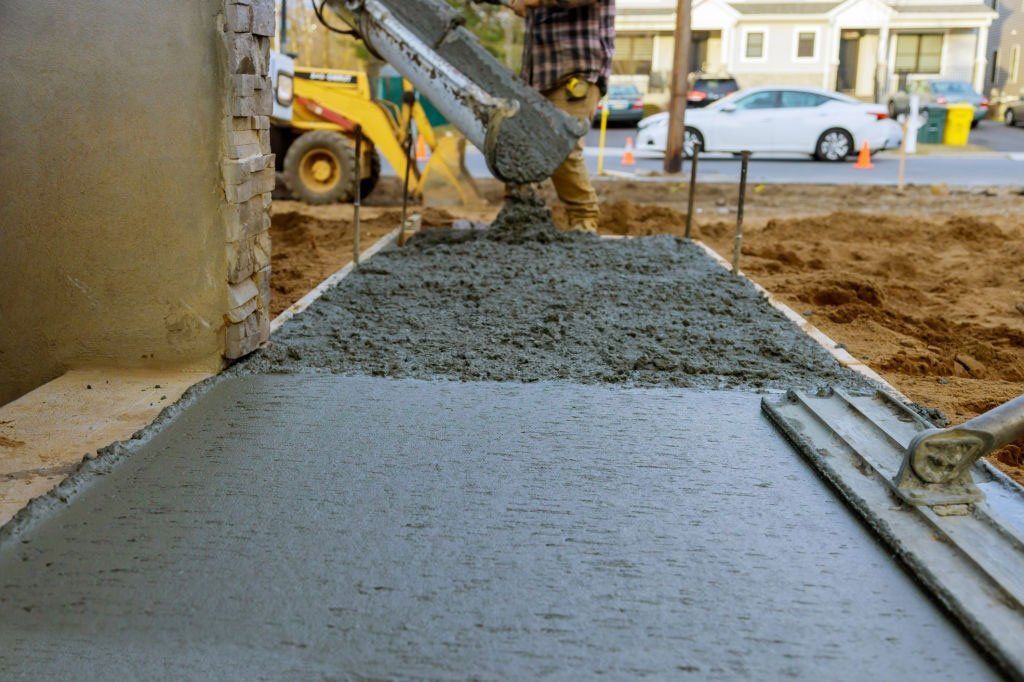
The concrete thickness of a parking lot will depend on the traffic and size of the space. A parking lot can be as thin as four inches, while a high-traffic area can require twelve inches. The thickness is determined by several factors, including the area's climate and traffic volume. A qualified contractor can help you choose the exact thickness of the cement in your parking lot.
Here are some standard measurements for determining the thickness of parking lot cement: In most cases, a parking lot is constructed by the ACI 330R-08 guide. This document specifies the minimum thickness of the pavement and the depth of the subgrade, but it does not determine the exact subgrade thickness for parking lots. Parking lots should be five inches thick, with at least 12 inches of subgrade beneath them. Some areas, such as around loading docks and dumpster pads, may need an additional 12 inches of concrete. Parking lots should be thicker to accommodate heavyweight trucks and other vehicles.
Various factors play a role in determining the thickness of the concrete slab. Parking lot designs differ for residential to commercial purposes. Truck stop parking requires thicker slabs than residential. Weight restrictions are also crucial in parking garages to ensure their longevity and safety. Additionally, structural engineers need to consider the possibility of excessive loading during construction and ensure the parking lot is built to last. These factors may be addressed by adding wire mesh or rebar.
The thickness of a parking lot's concrete is crucial, as the surface has higher static loads than floors and streets. However, parking lots are not as critical as streets, so proper thickness is essential for maximum durability. Also, it is necessary to consider drainage and traction. If you need a parking lot with traction, you can consider installing a Laser Screed. This piece of equipment is capable of placing the concrete precisely.
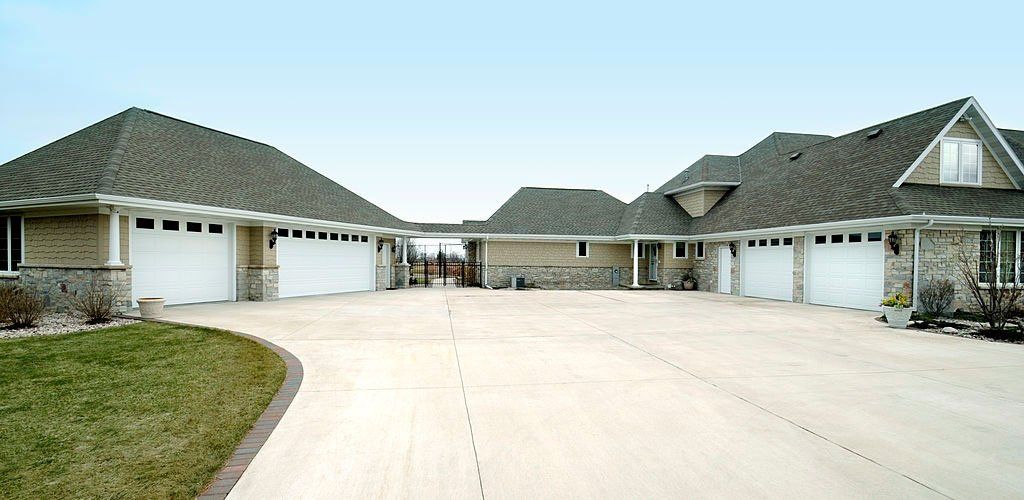
A cement parking lot is far more potent than asphalt and is less likely to experience severe cracking issues. Cement parking lots may occasionally break, but these cracks will be less consistent than asphalt. This is one of the main benefits of cement over asphalt. Asphalt parking lots are prone to potholes, depressions, and ripples, but cement parking lots are more resilient. With regular maintenance, you can make them stronger.
The thickness of a parking slab varies widely, but the thickness of a concrete slab should be four to twelve inches. The minimum thickness of parking slabs for light and medium-weight vehicles is six inches. If you have heavy-duty vehicles, the minimum thickness should be eight to twelve inches. If you need a thicker parking slab, you can go up to twelve inches. However, it is essential to remember that the thickness of parking slabs will depend on the span, loading condition, and engineering of the construction.
You might also like
Blog


Book a Service Today
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
Copyright Concrete Guys Hampton | Proudly Powered by Snapps